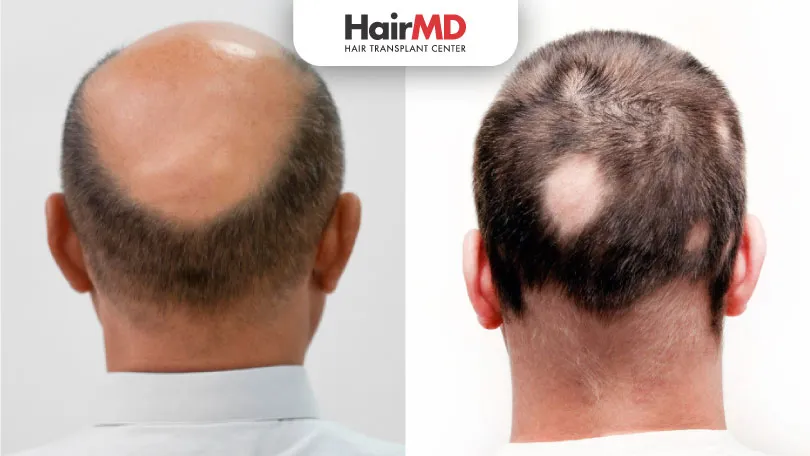
This condition is quite common, and we often come across questions related to Baldness and Alopecia in our practice. At our clinic, one of the most frequent concerns patients bring up is hair loss. They often use terms like “baldness” and “alopecia” interchangeably, which they might have come across online.
However, it’s important to distinguish between these terms to ensure appropriate treatment. Hence, we decided to create a detailed blog to help everyone understand these conditions thoroughly and choose the right treatment options.
What’s covered in the article?
- What is Baldness?
- What is Alopecia?
- Baldness and Alopecia
- Why differentiate Between Baldness and Other Forms of Alopecia?
- Treatment Strategies for Baldness and Alopecia
- Conclusion
What is Baldness?
Baldness, medically known as Androgenetic Alopecia, is a type of hair loss that specifically affects the top and front of the scalp. This condition is predominantly caused by genetic and hormonal factors. If you have a family history of baldness, you are more likely to experience this condition due to hereditary factors. Hormones such as androgens are responsible for hair loss. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone, specifically contributes to the shrinking of hair follicles, shortening the hair’s lifecycle and leading to thinning and loss.
What is Alopecia?
Alopecia is a broad term that covers hair loss on any part of the body. It includes various types, each with different symptoms and causes, expanding beyond just the scalp. Alopecia Areata, for example, manifests in patches and is often an autoimmune reaction where the immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles. Traction Alopecia is caused by constant pulling on the hair due to certain hairstyles. Telogen Effluvium is a temporary hair loss condition often triggered by stress or illness. Scarring Alopecia involves inflammation that destroys hair follicles and can cause irreversible hair loss.
Baldness and Alopecia
The doctor might ask for a few blood tests to get to the root cause of your hair loss. Hair loss can be caused due to multiple factors like nutritional deficiencies, hormonal imbalances, underlying illnesses etc. which can be detected on blood reports.
Why differentiate Between Baldness and Other Forms of Alopecia?
Understanding whether you are dealing with baldness or another form of alopecia is crucial because it directly influences the treatment options available. For instance, Androgenetic Alopecia, commonly known as baldness, often benefits from hormonal treatments or DHT blockers that specifically target the hormonal pathways involved in hair loss. On the other hand, Alopecia Areata, an autoimmune variant of alopecia, may require treatments that reduce immune system activity, such as immunosuppressive medications.
Identifying the correct Type of Hair Loss is vital because it helps tailor the treatment approach to be as effective as possible. This tailored approach not only improves the chances of successful hair regrowth but also minimizes unnecessary treatments that might not be effective for certain types of hair loss. For example, using immunosuppressive therapy in patients with Androgenetic Alopecia would not be beneficial and could lead to unnecessary side effects.
Treatment Strategies for Baldness and Alopecia
Treating baldness typically involves using medications such as minoxidil or finasteride. These drugs work by either promoting hair growth or by blocking the hormonal effects that cause hair loss. Minoxidil widens the hair follicle and prolongs the growth phase of hair, while finasteride inhibits the production of dihydrotestosterone, a hormone that contributes to hair loss in Androgenetic Alopecia.
In more severe cases where medical treatments do not yield the desired results, hair transplant surgery may be considered. This surgical procedure involves moving hair follicles from one part of the body to the balding areas, providing a more permanent solution to hair loss.
For other types of alopecia, such as Alopecia Areata or Traction Alopecia, the treatments often vary significantly. Corticosteroids might be used to treat Alopecia Areata by reducing inflammation around the hair follicles, thereby allowing hair to regrow.
In contrast, managing Traction Alopecia typically involves ceasing any physical stress on the hair such as tight hairstyles and possibly using gentle hair care routines to allow the scalp to recover.
The choice of treatment also depends on the underlying Cause Of The Hair Loss. For example, if stress is a major factor, as in Telogen Effluvium, then stress management techniques and lifestyle changes may be recommended as part of the treatment plan. Similarly, for autoimmune-related hair loss, besides corticosteroids, other immunomodulatory treatments may be considered to control the body’s immune response.
DO YOU KNOW?
Nearly 250 Patients Visit HairMD
Everyday For Various Hair Concerns
(15+ Years Of Expertise. 4157+ Successful Hair Transplant)
Meet Our Dermatologists
Conclusion
Both baldness and different types of alopecia can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life, making it essential to diagnose the specific type correctly. By understanding the underlying causes and distinctions between these conditions, patients can choose the most effective treatment methods and hopefully restore their hair and confidence.
We hope this detailed exploration helps clarify the differences and similarities between baldness and alopecia, ensuring our readers are well-informed to discuss their conditions with healthcare providers accurately.
Further Reading
How to Remove Dandruff in One day with Home Remedies?
Want quick dandruff relief? Simple home remedies to reduce flakes, itching, and scalp buildup in one day safely.
Top Hair Growth Treatments for Women: Your Ultimate Guide
Find effective hair regrowth treatments for women. Explore solutions like PRP, medications, and more to combat hair loss with expert advice from HairMD.
Relation Between Masturbation and Hair Loss
Is there a relation between masturbation & hair loss? Uncover truth with our detailed analysis, separating fact from fiction to provide clarity on this common concern.
Biotin for Hair: Effective or Overrated? | HairMD Pune
Biotin is popular for hair growth, but does it really work? Find out what HairMD Pune experts reveal about its benefits and limitations.
Have thoughts? Please let us know
We are committed not only to treating you, but also educating you.










